HSN Code Finder
Easily find the HSN Code (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) or ITC HS Code along with their applicable GST rates for your product using our HSN Code Search Tool. You can search by either the product name or the HSN Code itself. Alternatively, browse through our categorized list to find the HS code for your product.
This tool simplifies the process of identifying the correct code and understanding the GST rates that apply to your goods or services.
Overview
The Harmonized System Nomenclature (HSN) Code is a globally standardized system established by the World Customs Organization (WCO) to categorize goods. Its main aim is to ensure consistent and uniform product classification across countries, enabling smooth and transparent international trade while simplifying the management of global transactions.
Purpose and Significance of the HSN Code
The HSN Code serves several vital functions in both domestic and international trade:
1. Facilitating International Trade: By offering a standardized system, the HSN Code helps streamline product identification and classification across borders, making global trade more efficient.
2. Determining Taxes and Duties: The HSN Code is crucial for determining the correct duties, taxes, and customs fees for specific products, ensuring accurate processing of imports and exports.
3. Trade Data and Compliance: The code aids in gathering global trade statistics and ensures compliance with international regulations, supporting smooth transactions worldwide.
4. GST Classification in India: Under India’s Goods and Services Tax (GST) system, the HSN Code helps classify goods for proper taxation, ensuring consistency in tax filings and reducing errors.

Structure of HSN Code
In India, the HSN Code is an 8-digit classification system used under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework. Here’s an explanation of how the HSN code is organized, using the example of the HSN code 62.13.90.10 for handkerchiefs made from textile materials:
● First two digits (62): Indicate the Chapter number, which in this instance corresponds to articles of apparel and clothing accessories, excluding knitted or crocheted items.
● Next two digits (13): Represent the Heading number, specifying handkerchiefs.
● Following two digits (90): Denote the Product Code, providing a more detailed classification for textile-based handkerchiefs.
● Last two digits (10): Indicate the Tariff Item, offering further product details, such as the material used, for instance, whether it’s made of synthetic fibers.
The structure of the HSN code is as follows:
● Chapter (2 digits): Represents a broad category of goods, such as textiles, machinery, and other industries.
● Heading (2 digits): Specifies a more detailed classification within the chapter, like handkerchiefs or other specific items.
● Product Code (2 digits): Provides a further breakdown, detailing the specific type or variant, such as handkerchiefs made from textiles.
● Tariff Item (2 digits): Offers the most specific classification, which may include additional attributes like material composition or intended use.
HSN Section-wise Code List
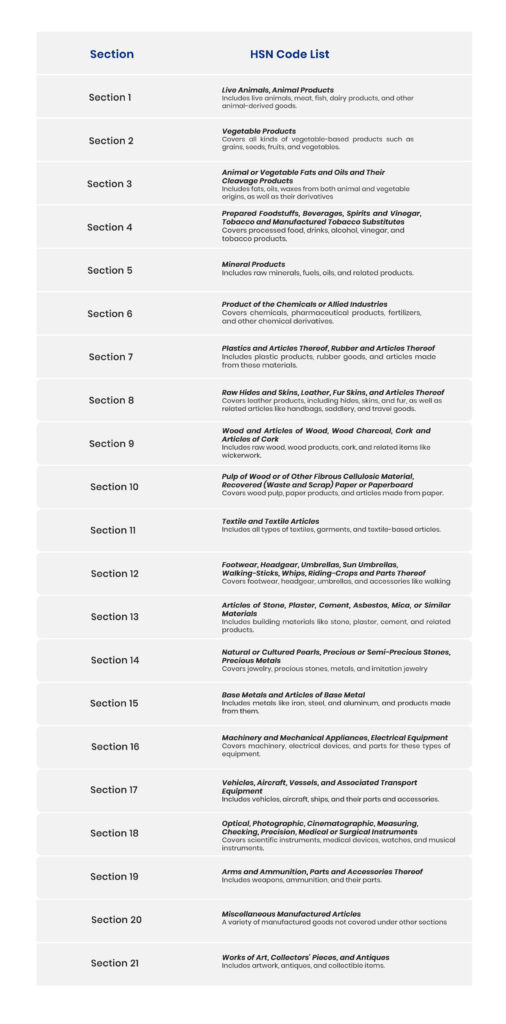
HSN in GST
From April 2021 onward, the Indian government mandated the inclusion of HSN (Harmonized System of Nomenclature) codes for goods and SAC (Services Accounting Code) for services in GST return filings. The number of digits required in the HSN/SAC codes varies according to a business’s annual turnover. Below is a summary of the HSN/SAC code declaration requirements based on transaction thresholds:
|
Transaction Charges |
Number of Digits of HSN to be Declared |
|
Up to ₹1.5 crore |
No HSN/SAC code required |
|
₹1.5 crore to ₹5 crore |
2-digit HSN code required |
|
More than ₹5 crore |
4-digit HSN code required |
HSN Code for Goods and Services under GST

Why is the HSN Code Required
The HSN code is essential for the GST system for several reasons:
1. Clarity on GST Rates: HSN codes help in the accurate classification of goods and services, ensuring that the correct GST rates are applied to specific products. This reduces the chances of errors in tax calculations and ensures uniformity across transactions.
2. Simplifies Tax Compliance: By using HSN codes, both taxpayers and tax authorities can easily identify the goods or services being transacted, leading to better transparency and easier tax filing.
3. Mandatory for Specific Cases: The requirement to mention HSN codes depends on the taxpayer’s annual turnover and the type of transaction. Here’s when HSN codes are mandatory:
● 6-digit HSN Code: Required for businesses with an annual turnover above ₹5 crore for all invoices (both B2B and B2C).
● 4-digit HSN Code: Required for B2B supplies by businesses with turnover up to ₹5 crore.
● Optional for Turnover Below ₹1.5 Crore: Businesses with turnover below ₹1.5 crore are not required to declare HSN codes in their invoices, although they may choose to do so.
In summary, the HSN code ensures that businesses comply with GST requirements, apply the correct tax rates, and provide clear and accurate invoices to customers, helping maintain transparency in the tax system.
Services Accounting Code (SAC) in GST
SAC (Services Accounting Code) is a unique 6-digit code used to classify services under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system. Similar to how HSN codes are used for goods, SAC codes are essential for identifying and categorizing the specific services provided by businesses.
Structure of an SAC Code:
Let’s break down an example SAC Code: 995431 (Demolition Services):
1. First Two Digits (99): These represent the Chapter and are common to all SAC codes, indicating that the code is related to services.
2. Next Two Digits (54): These represent the Heading of the major service category. In this case, it points to a specific category of services (e.g., demolition services, which may fall under a broader heading related to construction or repair services).
3. Last Two Digits (31): These represent the Service Code within the heading, providing a more specific identification of the nature of the service (e.g., demolition).
Application of HSN Code
1. HSN Code in International Trade: HSN codes ensure accurate classification of goods across countries, determining applicable tariffs, trade policies, and providing consistent international trade statistics. They reduce ambiguities and facilitate smoother global trade.
2. HSN Code in Domestic Taxation (GST): In India’s GST system, HSN codes are used to classify goods for taxation, ensuring uniform application of GST rates and simplifying tax compliance for businesses. They help reduce tax-related disputes and make the process clearer and more efficient.
3. HSN Code in Customs Procedures: Customs authorities use HSN codes to identify products, apply correct duty rates, and ensure compliance with trade regulations. This prevents revenue loss and ensures that duties are correctly levied on imported and exported goods.
In essence, HSN codes are essential for accurate classification, proper taxation, and smooth customs procedures, both domestically and internationally.
Importance of HSN Code in Different Sectors
1. HSN Code in Import and Export: HSN codes simplify the import and export process by offering a uniform system for classifying goods. This ensures the correct duties and compliance requirements are applied, streamlining customs procedures and facilitating smoother international trade.
2. HSN Code in Manufacturing: Manufacturers use HSN codes to classify both raw materials and finished products, ensuring compliance with tax regulations under GST. This classification also aids in inventory management, cost calculation, and optimizing supply chain management, ensuring better operational efficiency.
3. HSN Code in Retail and Wholesale: Retailers and wholesalers depend on HSN codes to accurately classify their inventory. This is essential for determining the correct tax rates, managing stock effectively, and ensuring compliance with tax regulations for smooth business operations.
How to Determine the Correct HSN Code
1. Tools and Resources for HSN Code Lookup:
● Several online tools and government portals are available to help businesses find the correct HSN code for their products. These tools simplify the classification process by providing a searchable database of HSN codes, ensuring that businesses can easily identify the appropriate code for their goods.
● Online HSN Lookup Tools: These platforms allow users to search by product name, description, or category, making it quicker to find the right code.
● Government Portals: The GST portal and other government websites provide official resources to check the correct HSN codes, ensuring that businesses follow the proper classification.
2. Common Mistakes in HSN Code Classification:
● Incorrect Classification: Misclassifying products under the wrong HSN code can lead to incorrect tax calculations, causing businesses to pay the wrong GST amount.
● Compliance Issues: Incorrectly classified goods may result in non-compliance with tax regulations, potentially leading to penalties or audit issues.
● Legal Consequences: Persistent errors in classification could also lead to legal repercussions or disputes with tax authorities.
Challenges in HSN Code Compliance
1. Misclassification and Its Consequences: Incorrectly classifying goods under the wrong HSN code can lead to issues such as incorrect tax calculations, fines, legal complications, and trade disruptions. Businesses must ensure accurate classification to avoid these costly mistakes.
2. Case Studies on HSN Code Compliance Issues: Real-world cases highlight the importance of accurate HSN code usage:
● A textile company faced penalties and disallowed input tax credits due to misclassification.
● An electronics importer overpaid duties due to incorrect HSN classification, leading to financial losses and customs audits.
● A retailer had issues during an audit because of inconsistent HSN code application, resulting in tax reassessments.
FAQ
The terms “HS Code” and “HSN Code” are closely related, but they are not identical. The HS Code is a globally recognized system for classifying goods, while the HSN Code is a more specific adaptation used in India. Under GST regulations, the HSN Code extends the HS Code to 8 digits, allowing for a more detailed categorization of products.
To find the correct HSN Code for a product, you can utilize online HSN lookup tools, browse official government databases, or seek assistance from a tax consultant. Proper classification is crucial for compliance with tax laws and accurate GST filings
Using an incorrect HSN Code can result in fines, penalties, and legal repercussions.
Certain goods may be exempt from HSN Code requirements based on specific regulatory guidelines.
HSN Codes influence the tax rates and duties applied to products, which ultimately affect their final pricing.
