Patent Registration (Complete Specification)
● File for Patent Registration online and protect your inventions for up to 20 years.
● Fastest patent filing in India—get your application submitted within 7 days.
● Accurate and efficient filing by Registered Patent Agents, ensuring a 100% safe process.
Complete Specification Application Process
● Day 1
Document submission and verification.
● Day 3
Discussion on application drafting and patent specification.
● Day 5
Finalization and submission of the patent application.
- What is a Patent?
A patent grants an individual or business exclusive rights to protect their invention from unauthorized importing, manufacturing, or selling. Consequently, this legal protection ensures that others cannot profit from the invention without the patent holder’s permission. In order to safeguard their innovative ideas, inventors often choose to file for a patent.
Filing a patent in India, however, can be a complex and time-consuming process. That being said, Vakilsearch offers a hassle-free solution for patent registration, thereby helping inventors complete their registration quickly and efficiently.
- Patent in India
The Patents Act, 1970, which was amended in 2005 to align with global standards, governs patent registration in India. Under this Act, patents are granted for innovations that are novel, inventive, non-obvious, and industrially applicable.
The Indian patent application process, on the other hand, involves several stages. These stages include filing the application, undergoing examination, and eventual publication. After the review, the patent claim may either be approved or rejected, depending on the outcome of the examination.
Once a patent is granted, it provides the patent holder with exclusive rights to manufacture, market, and use the invention for a specified period, typically up to 20 years. Consequently, this exclusivity ensures protection of the invention against unauthorized use by others.
- What Is Patent Registration?
Patent registration in India is a legally complex process that grants exclusive rights to an inventor or creator over their invention. Specifically, the government issues a patent for a fixed period—typically 20 years—to prevent others from making, using, or selling the invention without the patent holder’s consent.
In exchange for these exclusive rights, however, the patent owner is required to publicly disclose the complete details and specifications of the invention. This requirement, in turn, fosters further research and development by others in the field.
Moreover, GTS simplifies the patent filing process by offering expert support and a seamless online registration service, ensuring a smooth and efficient experience for all applicants. As a result, inventors can navigate the complexities of patent registration with ease and confidence.
- What Can Be Patented in India?
In India, patents can be granted for inventions related to products, processes, and methods. This includes a wide range of innovations such as chemicals, drugs, pharmaceuticals, software, and other advancements or improvements to existing technologies.
For an invention to be eligible for patent registration, it must meet the following criteria:
● Novelty: The invention must be new and not previously disclosed.
● Non-obviousness: The invention must not be obvious to someone skilled in the field.
● Industrial Applicability: The invention must have practical utility or be applicable in an industry.
If an invention meets these requirements, it may be eligible for patent protection in India.
- What Kind of Inventions Cannot be Patented in India?
In India, the following inventions cannot be patented:
● Natural laws or scientific principles (e.g., abstract theories)
● Aesthetic creations (e.g., literary, artistic, or musical works)
● Mental activities, games, or business methods (e.g., strategies for playing games or conducting business)
● Inventions against public morality or order (e.g., offensive or unethical inventions)
● Harmful inventions (e.g., those that pose a risk to the environment, animals, or humans)
These exclusions ensure patents are granted only for innovations that are beneficial and ethical.
- Importance of Patent Registration
Patent registration in India offers several key benefits:
● Exclusive rights: Grants the inventor or owner exclusive rights to their invention.
● Prevention of unauthorized use: Allows the patent holder to prevent others from making, using, or selling the invention without permission.
● Commercial opportunities: Provides the ability to sell, license, or transfer the patent to others.
● Legal protection: Enables the patent holder to seek compensation and take legal action against those who infringe on their patent.
● Encourages innovation: Stimulates research, development, and innovation, contributing to economic growth.
- Eligibility Criteria for Patent Register
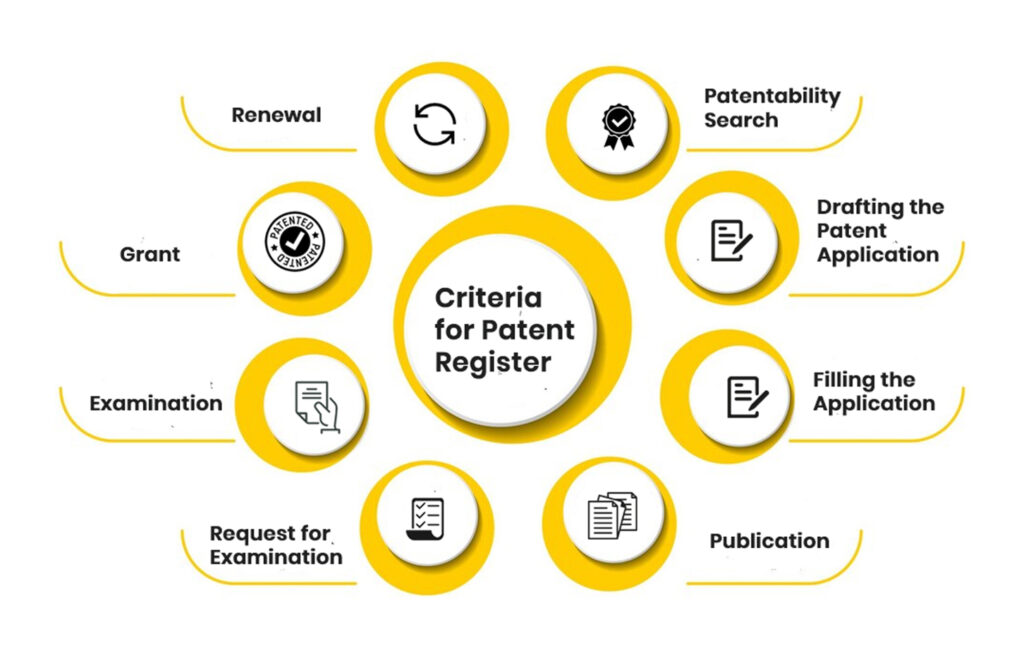
- Documents for Filing Patent Registration Application
To file a patent registration application in India, the following documents must be submitted:
● Complete Specification: A detailed description of the invention, including how it works and its potential applications.
● Provisional Application: A provisional application that provides an initial filing, if a complete specification is not ready at the time of filing.
● Declaration of Inventorship and Ownership: A statement declaring the inventors and confirming the ownership of the invention.
● Drawings and Diagrams: If applicable, include diagrams or drawings that illustrate the invention’s design or functionality.
● Applicant Details: Information about the applicant or owner of the invention, including their name, address, and contact details.
- Forms Required for Patent Registration Application
To register a patent in India, the following forms must be submitted to the Indian Patent Office:
Form 1: The primary application form for the grant of a patent. It includes details of the applicant, the invention, and the claims made regarding the invention.
Form 2: This form provides information about any priority application filed earlier by the applicant, if applicable.
Form 3: This form is used to disclose details of the inventors of the patent.
Form 5: Used to provide details if the patent is to be assigned to a government undertaking, including the specific assignment.
Form 26: This form is used when the applicant claims exclusive marketing rights for the invention, indicating details of such rights.
- Where to File a Patent Application?
In India, a patent application is filed at the appropriate patent office using Form-1 along with a provisional or complete specification, and the required fee. The jurisdiction of the patent office is determined based on the following factors:
● Applicant’s Place of Residence or Business: The jurisdiction is typically determined by the applicant’s place of residence, domicile, or business. In the case of joint applicants, the place of residence or business of the first mentioned applicant is considered.
● Origin of the Invention: The location where the invention was conceived or originated can also affect the jurisdiction.
● Foreign Applicants: If the applicant is a foreign entity with no business or domicile in India, the jurisdiction is based on the designated address for service in India.
Considering these factors ensures that the patent application is filed with the correct patent office, leading to a smoother and more efficient registration process.
Trademark vs Copyright vs Patent
Aspect
Trademark
Patent
Copyright
- Drafting of Patent Application
The process of drafting a patent application is intricate and requires both a thorough understanding of patent law and an in-depth knowledge of the invention. A well-drafted patent application must be clear, precise, and in full compliance with the Indian Patent Act, 1970. Below are the key components of a patent application:
● Title:
The title should be clear, concise, and descriptive of the invention, accurately reflecting its purpose or function.
● Abstract:
The abstract is a brief summary of the invention, typically no more than 150 words. It should capture the essence of the invention, explaining its core functionality in a succinct manner.
● Description:
The description provides a detailed explanation of the invention. It should cover all aspects of the invention, including how it works, its technical features, and potential applications. This section must contain enough information to allow someone skilled in the field to understand and replicate the invention.
● Claims:
The claims define the scope of protection for the invention. They should be clear, precise, and supported by the description. Claims outline the novel features of the invention and set boundaries for what the patent protects.
Each of these elements is crucial to ensuring the patent application meets legal standards and provides clear, comprehensive protection for the invention.
- Steps: Patent Registration Process
The patent registration process in India involves the following steps:
Step 1: File the Patent Application
Submit the patent application along with all required documents, including the complete specification, drawings (if applicable), and forms.
Step 2: Publication of the Application
Once filed, the patent application is published in the official Patent Journal, making it available to the public. This publication occurs typically after 18 months from the priority date.
Step 3: Request for Examination
After publication, the applicant must file a Request for Examination (RFE). The patent office will then conduct a thorough examination to assess the invention’s novelty, inventive step, and industrial applicability. The office will issue a Patent Examination Report.
Step 4: Patent Grant
If the patent office is satisfied with the examination report and finds the invention meets all requirements, it will grant the patent to the applicant.
The patent will be published, and the applicant will receive the patent certificate.
This process ensures that the invention is properly evaluated for patentability and, if approved, provides legal protection for the invention.
- Types of Patent Applications in India
In India, the following types of patent applications can be filed:
● Ordinary Application:
This is the most common type of application and is filed directly by the applicant with the Indian Patent Office. It is the standard route for registering a patent in India.
● Convention Application:
A Convention Application is filed by an applicant who has already filed a patent application in a convention country (a country that is part of an international agreement, such as the Paris Convention). This application allows the applicant to claim the filing date of the earlier application in the convention country.
● PCT International Application:
This application is filed under the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT), which allows the applicant to seek patent protection in multiple countries by filing a single international application.
The PCT system facilitates a unified patent application process recognized by all PCT member countries.
- What Is Patent Renewal?
● Patent renewal is the process of extending the validity of a granted patent by paying the prescribed renewal fee to the Indian Patent Office. Specifically, the renewal fee must be paid annually, starting from the 3rd year from the date of patent grant. Moreover, it is crucial that the fee be paid before the patent’s expiration date to maintain the protection afforded by the patent. If, however, the renewal fee is not paid on time, the patent will expire, and as a result, the invention will no longer have legal protection.
● What Is Patent Assignment?
On the other hand, patent assignment is the legal process by which the ownership of a patent is transferred from the original patent holder (assignor) to a new owner (assignee). This transfer is typically executed through a patent assignment agreement, which serves as a formal contract outlining the terms and conditions of the assignment. Once the assignment is completed, the new owner, consequently, gains all the rights associated with the patent, including the exclusive right to exclude others from using, making, or selling the patented invention.
- Recent Amendments to the Patent Act, 1970
The most recent amendments to the Patent Act, 1970 were made in 2019, and they introduced several significant changes to enhance the patent system in India. The key amendments include:
● Inclusion of Software and Business Methods:
Software and business procedures are now eligible for patent protection, provided they meet the basic requirements of novelty, inventive step, and industrial applicability.
● Extension of Patent Term for Pharmaceuticals:
The patent term for pharmaceutical products was extended from 20 years to up to 25 years, with an additional 5-year extension available, particularly for life-saving drugs.
● Expedited Examination:
A procedure for expedited examination was introduced, allowing applicants to fast-track the patent review process.
These amendments were designed to improve the patent filing process, encourage innovation, and align Indian patent laws with international standards, particularly in the areas of technology and pharmaceuticals.
- Why GTS?
GTS is a trusted partner for businesses and individuals seeking patent registration services. Here’s why:
● Experienced Team: GTS boasts a team of skilled and knowledgeable patent attorneys who guide you through the entire patent process—from patent searches to filing applications and securing your patent certificate.
● Comprehensive Services: They offer end-to-end services, ensuring that every step of the patent registration process is handled with precision and expertise.
● User-Friendly Platform: With GTS’s online platform, you can easily track the status of your patent application, making the process hassle-free.
● Competitive Pricing: GTS provides transparent pricing and competitive fees, ensuring that you get great value for your investment without any hidden costs.
● Reliable Protection for Innovation: GTS’s patent registration services are designed to protect your innovative ideas and inventions, making it a smart choice for businesses and individuals looking to secure their intellectual property.
GTS’s focus on professionalism, transparency, and customer satisfaction makes it an ideal choice for securing your patents and protecting your intellectual property.
- FAQs on FSSAI Registration/License
A patent can be filed by the inventor(s) or their assignee(s) (the person or entity who has received the rights to the invention). The application can be made individually or jointly with others who have contributed to the invention.
The three types of patents are:
Utility Patents: For new inventions or functional improvements.
Design Patents: For new and original ornamental designs.
Plant Patents: For new, asexually reproduced plant varieties.
Each type protects different aspects of innovation: functionality, appearance, and plant development.
In India, a patent is valid for 20 years from the date of filing the application. However, to maintain the validity of the patent, the annual renewal fees must be paid starting from the 3rd year.
Patent registration in India is important as it protects the inventor’s exclusive rights, provides legal protection against unauthorized use, and encourages innovation by granting a temporary monopoly. It also allows inventors to monetize their creations through licensing or selling the patent.
To apply for international patent registration in India, you can use the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) route. The process involves:
Filing a PCT application with the Indian Patent Office.
WIPO processes the application and conducts an international search and examination.
After the international phase, you can enter the national phase in India and other member countries for patent protection.
This simplifies applying for patents in multiple countries with a single application.
The main criteria for checking the patentability of an invention are:
Novelty: The invention must be new and not previously disclosed.
Inventive Step: It must involve a non-obvious innovation.
Industrial Applicability: It must be useful and applicable in industry.
No, a patent application is not automatically examined. The applicant must submit a request for examination and pay the associated examination fees. Only after this request is made will the patent office proceed with the examination of the application.
To register a patent online in India:
Create an account on the Indian Patent Office’s website.
Prepare the required documents (application form, invention details, drawings).
File the application and upload the documents on the portal.
Pay the filing fees online.
Submit the application for processing.
The Indian Patent Office will acknowledge the submission and proceed with the application.
Get Started with Global Consultants
Take advantage of Hong Kong’s dynamic market and register your company today with Global Consultant.
Contact Us for more details and to get started with your incorporation process!
