Simple and Compound Interest Calculator
Wondering how much your savings can grow? Use GTS’s Simple and Compound Interest Calculator to quickly calculate your potential returns!
Compound Interest Calculator
Compound interest, often referred to as “interest on interest,” involves adding the accumulated interest back to the principal amount. This means that you earn interest on both the initial deposit and the interest that has already been accrued, which leads to faster growth of your investment.
The frequency of compounding (e.g., annually, quarterly, monthly) impacts how quickly the interest accumulates. The more frequent the compounding, the greater the overall interest.
Example:
If you earn 10% annual interest on a ₹100 deposit, you would earn ₹10 after one year. However, with compound interest, you would earn interest not just on the ₹100 but also on the ₹10 interest already earned, leading to higher returns over time.
You can easily calculate your compound interest using the GTS Compound Interest Calculator. Just enter the principal amount, interest rate, time period, and compounding frequency to see how much your money will grow!
How Does a Simple Compound Interest Calculator Work?
A Compound Interest Calculator helps you understand how your investment can grow over time due to the compounding effect. Here’s how it works:
1. Interest Accumulation: Compound interest starts when your investment begins earning interest. The interest is added to the principal amount, and the next interest calculation is based on both the original principal and the accumulated interest.
2. Reinvestment of Interest: Each time interest is added to the principal, it begins to earn interest itself. This creates a cycle where your money continues to grow without any additional input, except for the compounding process.
3. Exponential Growth: As the investment compounds, the interest is calculated on an ever-growing amount, meaning your returns accelerate over time.
Key Factors that Influence Compound Interest:
● Time: The more time your money is allowed to compound, the more it grows. The longer the investment period, the greater the effect of compounding, leading to higher returns.
● Interest Rate: A higher interest rate means your money will grow faster. The higher the rate at which your investment compounds, the greater the returns over time.
By inputting your principal, interest rate, time period, and compounding frequency into a compound interest calculator (like the one at GTS), you can see how your money will grow over time and understand the powerful effect of compound interest on your savings.
Benefits of Compound Interest
● Accelerated Wealth Building: Compound interest boosts the growth of your investments over time, allowing your money to grow exponentially.
● Small Contributions, Big Impact: Even modest and consistent deposits can lead to significant growth as compounding works on both the initial amount and previously earned interest.
● Passive Income Generation: With compound interest, your money continues to grow without requiring constant input, effectively making your investment work for you.
● Perfect for Long-Term Savings: This strategy is ideal for achieving long-term financial objectives like retirement savings, as the power of compounding becomes increasingly effective over the years.
● Faster Goal Achievement: By compounding your returns, you can reach your financial milestones sooner without needing additional investments.
● Low-Risk Wealth Growth: Compound interest offers a reliable way to grow your savings without exposing you to high levels of financial risk.
● Promotes Regular Saving: It encourages consistent saving habits, as every contribution earns interest, fostering disciplined financial planning.
● Protects Against Inflation: Compounding helps your savings grow faster than inflation, preserving and increasing your money’s purchasing power.
● Builds a Safety Net: Over time, the growth from compound interest creates a financial cushion, offering peace of mind and security against unforeseen expenses.
Formula to Calculate Compound Interest
To calculate compound interest accurately, use the following formula:
A=P(1+rn)ntA = P \left( 1 + \frac{r}{n} \right)^{nt}A=P(1+nr)nt
Where:
A = The amount of money accumulated after n years, including interest.
P = The principal amount (the initial investment).
r = The annual interest rate (decimal form, so 10% = 0.10).
n = The number of times the interest is compounded per year (e.g., annually, quarterly, monthly).
t = The time the money is invested or borrowed for, in years.
This formula helps calculate the total amount (principal + interest) after a given time period, based on how often the interest is compounded.
Formula to Calculate Simple Interest
To calculate simple interest, use the following formula:
A=P(1+rt)A = P \left(1 + rt\right)A=P(1+rt)
Where:
A = The total amount (principal + interest).
P = The principal amount (the initial investment or loan).
r = The annual interest rate (as a decimal, so 10% = 0.10).
t = The time the money is invested or borrowed for, in years.
This formula calculates the total amount owed (or earned) by adding the interest to the principal, with interest calculated only on the original amount, not on accumulated interest.
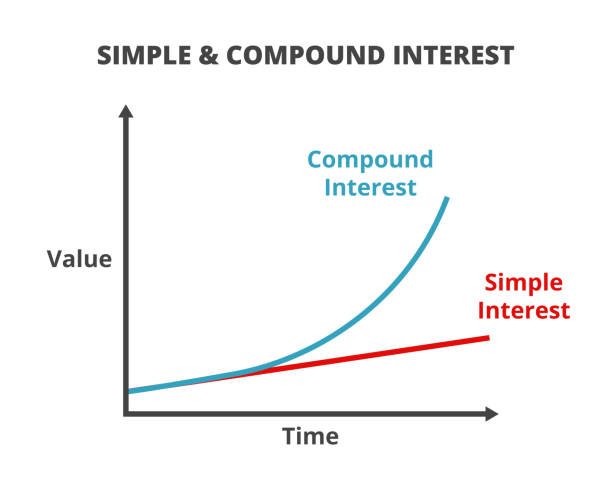
Simple Interest vs Compound Interest Calculator
Both Simple Interest and Compound Interest have their own benefits, depending on the investment or loan situation. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
| Interest Calculation: Interest is calculated only on the initial investment (principal). |
| Principal Amount: The principal remains constant throughout the investment period. |
| Growth Rate: The growth is linear (fixed interest on the same principal). |
| Ideal for: Short-term loans or simple investments where you don’t need to earn interest on your interest. |
|
Interest Calculation: Interest is calculated on both the original principal and the accumulated interest. |
|
Principal Amount: The principal amount increases after each compounding period as interest is added to the original investment. |
|
Growth Rate: The growth is exponential (interest accumulates on interest over time). |
|
Ideal for: Long-term investments, like retirement savings, where you want your money to grow faster through compounding. |
Applications of Simple Interest
Simple interest is widely used in various financial scenarios, especially when the interest is calculated only on the principal amount. Here are some common applications of simple interest:
Loans:Lenders, such as banks and financial institutions, use simple interest to calculate the interest that borrowers owe on personal loans, car loans, and other short-term loans. The interest is charged only on the original loan amount.
Investments:Investors use simple interest to calculate the returns they earn on fixed deposits, savings accounts, or other low-risk investments. The interest is paid based on the original principal, not on accumulated interest.
Mortgages:Some types of mortgages, especially in the case of short-term loans, may use simple interest to determine how much interest the borrower owes in addition to the principal over the loan term.
Credit Cards:Credit card companies often use simple interest to calculate the interest owed on outstanding balances. The interest is computed based on the principal amount (the balance) of the cardholder’s debt.
While simple interest is easier to calculate and understand, it’s generally used for shorter-term loans or investments. For longer-term financial products, compound interest is more common as it offers the benefit of interest on interest, which results in faster growth of investments or higher debt accumulation.

Advantages of Using a Simple Interest Calculator
Benefits of Using a Simple Interest Calculator
A Simple Interest Calculator is an essential tool for calculating interest amounts effortlessly and accurately. Whether for loans, investments, or other financial planning, it offers several key advantages:
User-Friendly Design: Simple interest calculators are easy to use, requiring just basic inputs like the principal amount, interest rate, and time period. This makes them suitable for both beginners and financial experts.
Precise Calculations: By entering accurate data, the calculator ensures you get exact interest amounts, total repayments, or potential returns, eliminating the risk of manual errors.
Wide Applicability: These calculators can be used for diverse financial needs, including loans, savings, investments, and mortgages. They simplify interest calculations across different scenarios.
Effective Comparison Tool: Adjusting variables like principal, interest rate, or time period allows you to compare various financial options. This enables you to make informed choices aligned with your financial objectives.
Using a simple interest calculator saves time, enhances accuracy, and supports smarter financial planning, making it an indispensable resource for managing money effectively.
FAQ
A Simple Interest Calculator is useful for calculating returns on investments or loans where interest is only charged on the initial principal. However, when it comes to investing, compound interest is generally preferred for better long-term growth. Here’s why:
Simple Interest: Grows at a linear rate, meaning interest is calculated only on the principal amount. It’s suitable for short-term loans or investments, but not ideal for long-term wealth building.
Compound Interest: Allows interest to be calculated on both the principal and the interest earned, leading to exponential growth over time. This is why compound interest is typically favored for investments like mutual funds, retirement savings, and long-term deposits.
Yes, a Simple Interest Calculator is very easy to use. You can quickly calculate the interest on a loan or investment by entering just a few key details:
Principal Amount (the initial investment or loan amount)
Rate of Interest (the interest rate)
Time Period (the duration for which the money is invested or borrowed)
A Simple Interest Calculator helps you determine:
Total Interest: Calculates interest based on the principal, interest rate, and time period.
Repayment Amount: Shows the total amount to be repaid, including both principal and interest.
Savings on Early Payments: Estimates savings if you pay off a loan early.
Interest on Short-Term Loans: Useful for calculating interest on short-term loans like personal and car loans, particularly interest-only loans.
It’s a simple tool for quickly calculating interest, planning loan repayments, and assessing short-term investment returns.
In simple interest, the rate refers to the rate of interest applied to the principal amount over a specific time period. It represents the percentage of the principal that will be charged or earned as interest, typically expressed annually. The rate of interest can vary depending on factors like the type of loan, the lender’s terms, or the investment product.
Simple interest is calculated solely on the initial principal or loan amount, while compound interest is calculated on both the original principal and the interest that has already been accumulated over time. This means that compound interest grows faster, as interest is added to the principal for each compounding period.
